Embark on a fascinating journey through the periodic table as we explore the captivating realm of "Periodic Trends in Properties of Elements." This exploration unveils the recurring patterns and behaviors that elements exhibit, shedding light on the intriguing variations in atomic and chemical characteristics. From electronegativity to atomic radius, witness how these trends shape the periodic landscape, providing crucial insights into the fundamental nature of the building blocks of matter. Join us in deciphering the language of periodicity, where the arrangement of elements unfolds a narrative of predictability and intrigue.
Exploring Periodic Trends in Elemental Properties
Periodic Properties of the Elements:
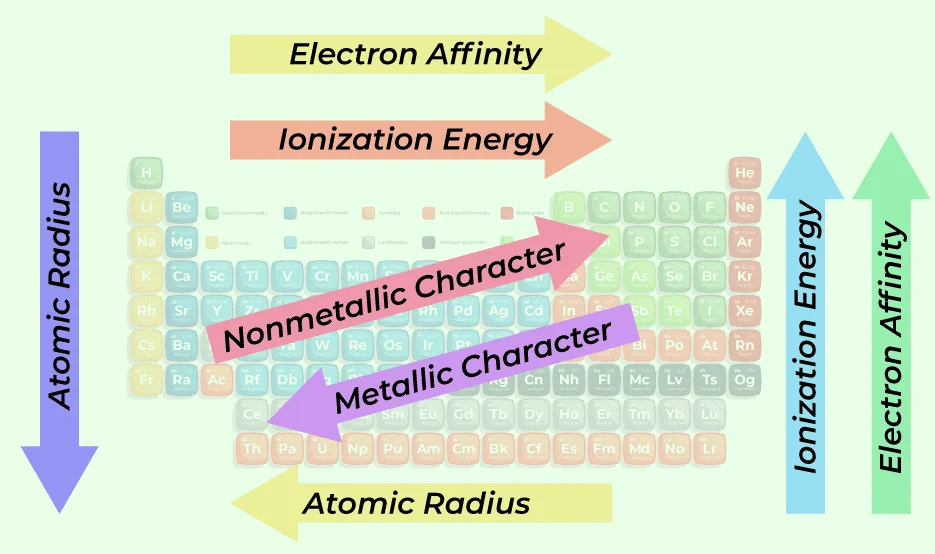
Periodic properties of elements refer to the recurring trends or patterns in their physical and chemical characteristics as one moves across a row or down a column in the periodic table. These properties include:
-
Atomic Radius: The size of an atom, which generally decreases across a period and increases down a group.
-
Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom, usually increases across a period and decreases down a group.
-
Electron Affinity: The likelihood of an atom to accept an additional electron, often increases across a period and decreases down a group.
-
Electronegativity: The tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond, generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
-
Metallic Character: Elements become less metallic across a period and more metallic down a group.
-
Melting and Boiling Points: These generally increase across a period and decrease down a group.
Understanding these trends provides valuable insights into the behavior of elements, facilitating predictions about their reactivity, bonding tendencies, and physical properties.
The Periodic Law:
The Periodic Law is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. In simpler terms, when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their properties exhibit periodic patterns. This concept laid the foundation for the organization of the periodic table.
Key points related to the Periodic Law:
-
Mendeleev's Table: Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, is credited with the early development of the periodic table in the 1860s. He arranged elements based on increasing atomic mass and observed recurring patterns in their properties.
-
Modern Periodic Table: With the discovery of the proton and the understanding of atomic structure, the modern periodic table was developed, organizing elements by increasing atomic number.
-
Periods and Groups: Elements are arranged in periods (horizontal rows) and groups (vertical columns). Elements in the same group share similar properties due to similar electron configurations.
-
Periodic Trends: The Periodic Law is reflected in trends such as atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and others that repeat systematically across the periodic table.
-
Predictive Power: The Periodic Law allows scientists to predict the properties of undiscovered elements based on their positions in the periodic table.
The Periodic Law is a foundational concept in chemistry, providing a framework for understanding the relationships between the various elements and their behaviors in chemical reactions.
Periodic Trends:
Periodic trends encompass predictable variations in the properties of elements across the periodic table. Atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, and metallic character exhibit systematic changes. Moving left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases, while ionization energy and electronegativity increase. Down a group, atomic radius and metallic character increase, while ionization energy and electronegativity decrease. These trends result from the interplay of factors like effective nuclear charge, shielding, and electron configurations, offering valuable insights into the behavior of elements and their interactions in chemical reactions. Understanding periodic trends enhances the comprehension of elemental properties and reactivity.
Periodic Trends in Ionic Radii:
Periodic trends in ionic radii refer to the systematic variations in the size of ions as you move across a period or down a group in the periodic table. Key considerations include:
-
Across a Period (Left to Right):
- Cations (positive ions) formed by nonmetals are smaller than their parent atoms.
- Anions (negative ions) formed by metals are larger than their parent atoms.
-
Down a Group (Top to Bottom):
- Both cations and anions increase in size as you move down a group.
- This is mainly due to the addition of electron shells, which increases the overall size of the ion.
These trends are influenced by the effective nuclear charge, shielding effect, and number of electron shells. Ionic radii trends are essential for understanding the behavior of ions in chemical reactions and their impact on the properties of compounds.
Download Chemistry Notes
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES:
Q1: What are periodic trends in the properties of elements?
Answer: Periodic trends refer to the predictable patterns or variations in the physical and chemical properties of elements as you move across periods and down groups in the periodic table.
Q2: What is the atomic radius, and how does it change across the periodic table?
Answer: Atomic radius is the size of an atom. It generally decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a group.
Q3: How does ionization energy vary in the periodic table?
Answer: Ionization energy, the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, tends to increase across a period and decrease down a group.
Q4: What is the trend for metallic characters in the periodic table?
Answer: Metallic character decreases across a period and increases down a group. Metals exhibit a high metallic character, while nonmetals show a low metallic character.
Q5: What role does electron configuration play in periodic trends?
Answer: Electron configuration influences periodic trends by affecting factors such as shielding and effective nuclear charge, which in turn impact properties like atomic radius and ionization energy.

Download Question Bank


Post a Comment