Chemistry is the language of matter, and understanding its basic principles opens the door to a world of discovery and innovation. Whether you're a student taking your first steps into the realm of chemical knowledge or an enthusiast eager to delve deeper.
A Comprehensive Guide to Some Basic Concepts with CBSE NCERT Download
Unlocking the Wonders of Chemistry a Journey into Fundamental Concepts
Chemistry, often hailed as the central science, plays a pivotal role in unraveling the mysteries of the world around us. Whether you’re stepping into the captivating realm of chemistry for the first time or seeking a refresher. let’s embark on a journey through some basic concepts that form the bedrock of this fascinating discipline. At the heart of chemistry lies the atom – the infinitesimal particle that constitutes matter. Picture a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons. Take a deep breath and delve into the gas laws and fundamental principles that govern the behavior of gases. From Boyle's Law to Charles's Law. where substances transform into entirely new entities. Understand the key components of a reaction – reactants and products – and explore the different types of reactions that occur in both the laboratory and the world around us.

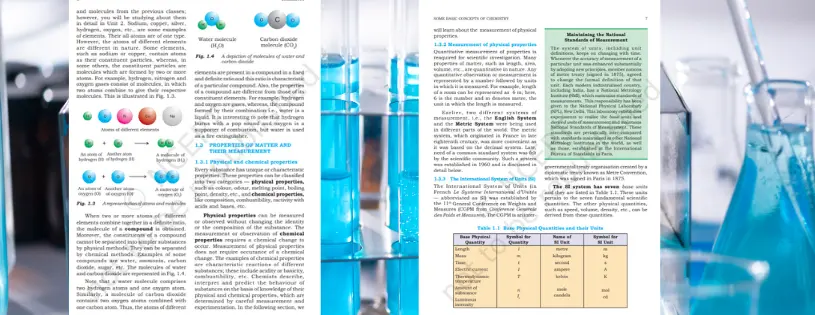
Atoms
- At the heart of chemistry are atoms, the smallest units of an element.
- Each atom consists of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) and electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Elements
- Elements are substances composed of one type of atom.
- They are organized on the periodic table based on their atomic number.
Molecules
- Molecules form when atoms chemically bond. They can be simple, like O₂ (oxygen), or complex, like glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆).
Compounds
- Compounds are substances made up of different elements chemically combined in fixed ratios.
- Water (H₂O) is a common example of a compound.
Chemical Reactions
- Chemical reactions involve the breaking and forming of bonds between atoms.
- Reactants transform into products in a balanced equation.
Chemical Bonds
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Acids and Bases
- Acids release hydrogen ions (H⁺) in water, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
- The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution.
Download chemistry Notes
Understanding these basic concepts provides a solid foundation for exploring more advanced topics in chemistry. Whether you're intrigued by the behavior of atoms or the intricacies of chemical reactions, these fundamentals serve as the gateway to a deeper appreciation of the molecular world.
Exploring Chemistry Chapter 1 Some Basics Concepts of Chemistry in CBSE NCERT Class 11
CBSE Class 11 Board Exam Sample Paper: Test Your Knowledge in Chemistry Questions.

Download Sample paper
[Previous Year Question Solution Physics Download Button]
[Previous Year Question Solution Chemistry Download Button]
[Previous Year Question Solution Math Download Button]
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
FAQ
Q1: What is an atom?
Answer: An atom is the basic unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in orbit.
Q2: What is the Periodic Table?
Answer: The Periodic Table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number and properties. It provides a systematic way to understand the relationships between different elements.
Q3: What is the difference between an element and a compound?
Answer: An element is a substance composed of only one type of atom, while a compound is a substance formed by chemically bonding different elements in fixed ratios.
Q4: How do chemical bonds form?
Answer: Chemical bonds form when atoms interact. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, and covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Q5: What is a molecule?
Answer: A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together. It can be composed of one or multiple types of atoms.


Post a Comment