The Complete IB Chemistry Study Guide for SL & HL 2021
The IB Chemistry Guide and Notes for SL and HL to fetch you better scorers in the IB test is not going to be skyrocketing. But scrutiny would take you places. IB Chemistry is not too hard or too simple, but it all depends on how you look at it. More like it is how best you get hold of the syllabus and the study guide you are getting. We have crafted the best IB Chemistry Study Guide for SL and HL students.

This IB Chemistry Guide includes:
Get Free IB Chemistry Trial Session Download IB Chemistry eBook
Download IB Chemistry Guide Here
IB Chemistry Syllabus Guide
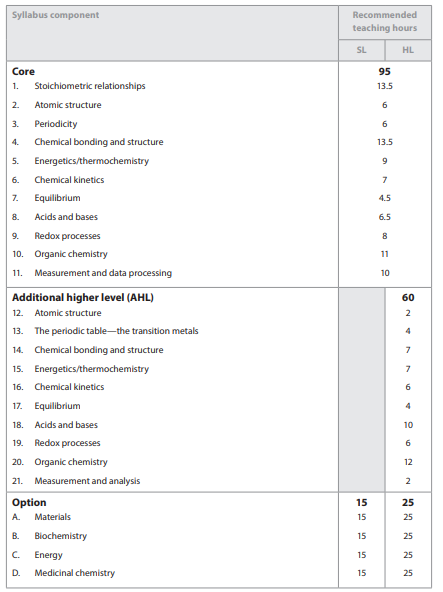
Download IB Chemistry Syllabus Here
IB Chemistry Resources
IB Chemistry Exam Overview Guide
|
|
Paper 1
|
Paper 2
|
Paper 3 (Options)
|
IA
|
|
Standard Level (SL)
|
30 multiple choice questions
|
45 min
|
20%
|
Short answers
|
1 hr 15 min
|
40%
|
Short answers
|
1 hr
|
20%
|
20%
|
|
Higher Level (HL)
|
40 multiple choice questions
|
1 hr
|
20%
|
Short answers
|
2 hr 15 min
|
36%
|
Short answers
|
1 hr 15 min
|
24%
|
20%
|
|
|
Periodic table only (supplied)
No calculators
|
Calculators and Data Booklet
|
|
IB Chemistry Exam Scoring Guide
Standard Level
Day 1- Paper 1 (30 MCQ / 45 Minumtes)
|
Mark Range
|
0-7
|
8-12
|
13-18
|
19-20
|
21-23
|
24-26
|
27-30
|
|
Grade
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
Paper 2 (Short Answers/ 1 Hour 50 Minutes)
|
Mark Range
|
0-7
|
8-12
|
13-18
|
19-20
|
21-23
|
24-26
|
27-30
|
|
Grade
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
Day 2- Paper 3 (Options / 1 Hour)
|
Mark Range
|
0-7
|
8-12
|
13-18
|
19-20
|
21-23
|
24-26
|
27-30
|
|
Grade
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
Higher Level
Day 1- Paper 1 (40 MCQ / 1 Hour)
|
Mark Range
|
0-7
|
8-12
|
13-18
|
19-20
|
21-23
|
24-26
|
27-30
|
|
Grade
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
Paper 2 (Short Answers/ 2 Hour 15 Minutes)
|
Mark Range
|
0-7
|
8-12
|
13-18
|
19-20
|
21-23
|
24-26
|
27-30
|
|
Grade
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
Day 2- Paper 3 (Options / 1 Hour 15 Minutes)
|
Mark Range
|
0-7
|
8-12
|
13-18
|
19-20
|
21-23
|
24-26
|
27-30
|
|
Grade
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
IB Chemistry Calculators Guide
IB Chemistry New Terminology Guide
Topic 1: Stoichiometric relationships 1.3
Pressure at STP redefined in data booklet: STP conditions = 273 K and 100 kPa; SATP conditions = 298 K and 100 kPa. Molar volume of an ideal gas at STP = 2.27 × 10−2 m3 mol−1 (= 22.7 dm3 mol−1)
Topic 4 : Bonding
4.3 Electron domains now used in place of negative charge centres. Coordinate bond exclusively used in place of dative bond
4.4 London (dispersion) forces used for instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces of attraction; Van der Waals’ forces redefined as an inclusive term to include dipole-dipole, dipole induced dipole and London (dispersion) forces
Topic 8 : Acids and bases
8.1 Amphiprotic species can act as Bronsted–‐Lowry acids and bases; amphoteric substances can act as acids and bases, including reactions where protons are not transferred. Topic 9 : Oxidation and reduction
9.1 Oxidation state uses Arabic numerals e.g. +2, ‐3; oxidation number uses Roman numerals in the nomenclature of a compound e.g. Fe(II)O. 9.2 Definition of electrochemical cell is now an inclusive term to include voltaic and electrolytic cells.
Topic 10 : Organic chemistry
10.1 Functional group refers to the part of a molecule responsible for specific properties e.g. –OH hydroxyl; class of compound refers to the family of compounds/homologous series e.g. alcohols.
Topic 13 : The periodic table – the transition metals
13.1 Transition element redefined to include scandium.
Topic 18 : Acids and bases
18.3 pH curves now used in place of titration curves.
Topic 20 : Organic chemistry
20.3 Cis-trans and E/Z isomerism used in place of geometric isomerism
IB Chemistry Group 4 Project Guide
The Group 4 Project is a compulsory activity that all IB Chemistry Diploma Programme students must be a part of. The main agenda of this assessment is to understand and analyse a Chemistry related issue and problem. This activity emphasises on the process and knowledge rather than "The Assessment"
IB Chemistry IA Overview Guide

Internal Assessment is one of the most important part of IB Diploma Chemistry course, which is compulsory for both Higher Level and Standard Level students. It helps students to exhibit the application of their skills and knowledge. The requirements and guidlines for both SL and HL students are the same. It contributes 20% to the final assessment.
IB Chemistry Internal Assessment (IA) Student Support Guide
Download IB Chemistry IAs Student Support Guide
IB Chemistry Internal Assessment Examples
|
Investigation
|
Title
|
Student Work Annotated
|
|
1
|
Factors effecting the boiling and melting points in organic homologous series
|
LINK
|
|
2
|
The effect of halogen atom substitution on bond angles in halogenated compounds
|
LINK
|
|
3
|
Positive inductive effect of methyl groups in nine simple alcohols
|
LINK
|
|
4
|
An investigation into the dependence of egg protein denaturation on temperature
|
LINK
|
|
5
|
Impact of increased water acidity on coral reefs based on a study of the kinetics of CaCO3 and HCl
|
LINK
|
|
6
|
A study of the saponification reaction of olive oil
|
LINK
|
|
7
|
Investigating the oxidative rancidity of polyunsaturated oils
|
LINK
|
|
8
|
The enthalpy of combustion of alcohols
|
LINK
|
|
9
|
Investigating lipids suitable for manufacturing soap for a school project
|
LINK
|
|
10
|
Effect of cooking time on chlorophyll degradation
|
LINK
|
|
11
|
Hydrolysis of PVA
|
LINK
|
|
12
|
Ion absorption properties of sodium polyacrylate
|
LINK
|
|
13
|
Catalysis of iodine clock reaction
|
LINK
|
|
14
|
Lattice enthalpy
|
LINK
|
|
15
|
Boiling points of binary mixtures
|
LINK
|
|
16
|
Effect of red wine tannin concentration on methylene blue oxidation
|
LINK
|
|
17
|
Oxidation of luminol
|
LINK
|
|
18
|
Reaction kinetics of hydrolysis of sucrose using polarimetry
|
LINK
|
IB Chemistry IA Scoring Guide
Duration: 10 Hours
Weightage: 20%
Internal Assessment Criteria
| Personal Engagement |
Exploration |
Analysis |
Evaluation |
Communication |
Total |
| 2 (8%) |
6 (25%) |
6 (25%) |
6 (25%) |
4 (17%) |
24 (100%) |
Download IB Chemistry IA Scoring Guide Here
IB Chemistry Notes for SL and HL
Both IB Chemistry SL and HL will cover the 11 topics in the order with same subtopics listed in the following IB Chemistry Guide discussions. (The time allotted in the bracket is only indicative).
Click on the links to find the respective Notes
1.1. Particulate Nature of Matter and Chemical Change
Key IB points to keep in mind
- Mixtures – Homogeneous or Heterogeneous.
1.2 The Concept of the Mole
Key IB points to keep in mind
- ‘n’- The mole is a fixed number of particles
- M (Molar mass) has the unit’s g mol-1."
- Compound – The empirical formula and molecular formula
Notes – Mole Concept and Avogadro’s Constant
Notes – Mole
Notes – Formulae’s
Notes – Chemical Equations
1.3 Reacting Masses and Volumes
Key IB points to keep in mind –
- Limiting or excess reactants
- Difference between the experimental and theoretical yield
- Avogadro’s law: mole ratio of reacting gases dependent on volumes of the gases.
Notes – Mass & Gaseous Volume Relationships in Chemical Reactions
Notes – Solutions
Notes – All of the Stoichiometry
2.1 The Nuclear Atom
Key IB points to keep in mind:
- "Atoms contain a positively charged dense nucleus composed of protons and neutrons (nucleons)."
Notes – Atom
Notes – Atomic Theory
2.2 Configuration of Electron
Key IB Points to keep in mind:
- The Sub-levels contain a fixed number of orbitals, regions of space where there is a high probability of finding an electron.
- "Each orbital has a defined energy state for a given electronic configuration and chemical environment and can hold two electrons of opposite spin."
Notes – Mass Spectrometer
Notes – Electron Arrangement

Key IB points to keep in mind
3.1 Periodic Table
3.2 Periodic Trends
Key IB points to keep in mind:
- The Vertical and horizontal trends in the periodic table exist for atomic radius, ionic radius, ionisation energy, electron affinity and electronegativity.
Topic 4: Chemical Bonding and Structure – 13.5 Hours for SL and HL
4.1 Ionic Bonding and Structure
- "The ionic bond is due to electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions."
4.2 Covalent Bonding
Key IB points to keep in mind
- "A covalent bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the positively charged nuclei."
- The Bond polarity results from the difference in electronegativities of the bonded atoms.
4.3 Covalent Structures
Key IB points to keep in mind
- Lewis (electron dot) structures show all the valence electrons in a covalently bonded species.
- The octet rule is the tendency of atoms to gain a valence shell with a total of 8 electrons.
- Some atoms, like be and B, might form stable compounds with incomplete octets of electrons.
4.4 Intermolecular Forces
Key IB points to keep in mind:
- Intermolecular forces include London (dispersion) forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding."
4.5 Metallic Bonding
Key IB points to keep in mind
- The metallic bond is an electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive ions and delocalized electrons.
Notes – Energetics
5.1 Measuring Energy Changes
Key IB points to keep in mind
- "Heat is a form of energy.
- The temperature measures of the average kinetic energy of the particles are needed to assess.
- "Total energy is conserved in chemical reactions."
- "Chemical reactions that involve the transfer of heat between the system and the surroundings are described as endothermic or exothermic."
- "The enthalpy change (∆H) for chemical reactions is indicated in kJ mol-1."
- "∆H values are usually expressed under standard conditions, given by ∆H°, including standard states."
5.2 Hess’s Law
Key IB points to keep in mind
- The enthalpy change of a reaction is carried out in some steps has equalised the sum changes for the individual steps.
5.3 Bond Enthalpies
Key IB points to keep in mind
- "Bond-forming releases energy and bond-breaking requires energy.
- "Average bond enthalpy is the energy needed to break one mole of a bond in a gaseous molecule averaged over similar compounds."
Get Free IB Chemistry Trial Session Download IB Chemistry eBook
6.1 Collision Theory and Rates of Reaction
Key IB points to keep in mind
- The Species react as a result of collisions of sufficient energy and proper orientation.
- "The rate of reaction is expressed as the change in concentration of a particular reactant/product per unit time.
6.2 Notes – Collision theory
6.3 Notes – Rates of Reaction

7.1 Equilibrium
Key IB points to keep in mind
- An equilibrium state is reached in a closed system when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal."
- The equilibrium law describes how the equilibrium constant (Kc) can be determined for a particular chemical reaction.
Notes – The position of Equilibrium
Study Guide – Equilibrium
Key IB points to keep in mind
- A pair of species differing by a single proton is called a conjugate acid-base pair."
8.2 Properties of Acids and Bases
Key IB points to keep in mind
- Most of the acids have observable characteristic chemical reactions with reactive metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides, hydrogen carbonates and carbonates.
- Salt and water are results in exothermic neutralisation reactions.
Study Guide – Acids and Bases
8.3 The pH Scale
Key IB points to keep in mind
8.4 Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
Key IB points to keep in mind
Notes – Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
8.5 Acid Deposition
Key IB points to keep in mind
Notes – Acid Deposition
9.1 Oxidation and Reduction
Key IB points to keep in mind
- An oxidizing agent is reduced, and a reducing agent is oxidized.
- Variable oxidation numbers exist for transition metals and most main-group non-metals.
- The activity series ranks metals according to the ease with which they undergo oxidation.
- The Winkler Methods used to measure biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), used as a measure of the degree of pollution in a water sample.
Notes – Oxidation and Reduction
Study Guide – Oxidation and Reduction
9.2 Electrochemical Cells
Key IB points to keep in mind
- Voltaic cells convert energy from spontaneous, exothermic chemical processes to electrical energy.
Notes – Electrochemical Cells


Post a Comment